


Because a black hole bends light if a photon leaves a person and travels towards the black hole, it could theoretically bend around and return to the person's eyes; this would make it possible for the person to see themselves in the past.
There are four known types of black holes: stellar-mass, supermassive, intermediate-mass, and primordial black holes.
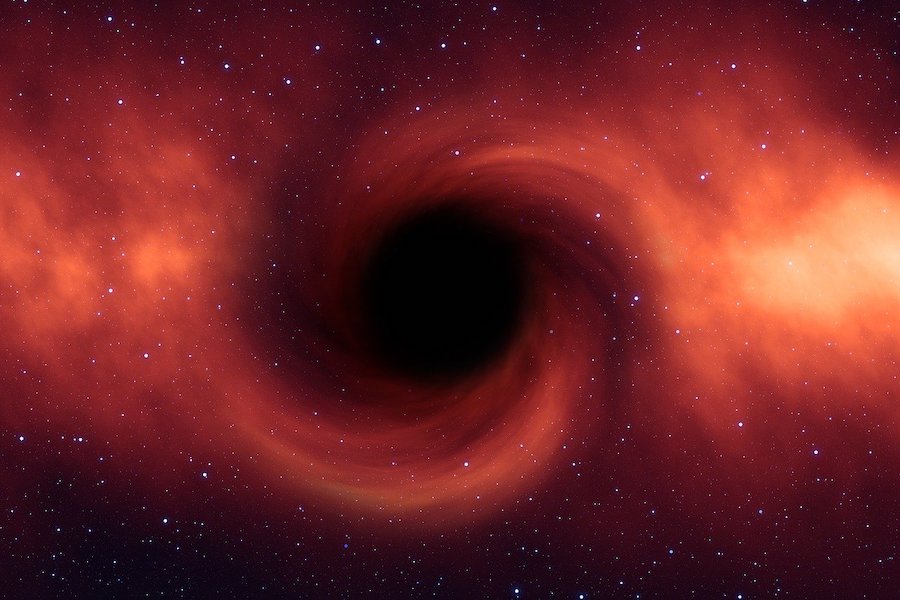

Though supermassive black holes are billions of times more massive than our Sun, they are less dangerous than stellar-mass ones. This is because the tidal forces at the event horizon of stellar-mass black holes are super violent. They are so dangerous that a living organism wouldn’t even survive a fraction of a second near them.

Some produce powerful jets of particles that travel at nearly the speed of light, often extending for thousands of light-years; these are called accretion disks. The longest accretion disk on any was measured on the quasar III Zw 002. The disc measured 52.4 light-days in length, more than the distance between the Sun and the Earth.
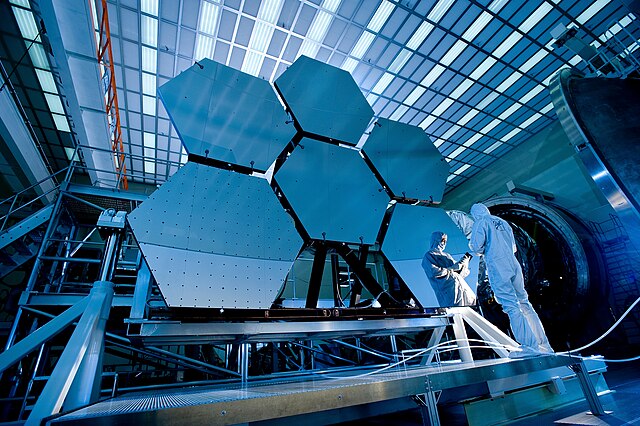

The James Webb Telescope recently discovered the oldest black hole ever observed by astrophysicists. The freak of nature, which resided in the GN-z11 Galaxy, was detected to have formed 400 million years after the Big Bang; this makes it about 13 billion years old.
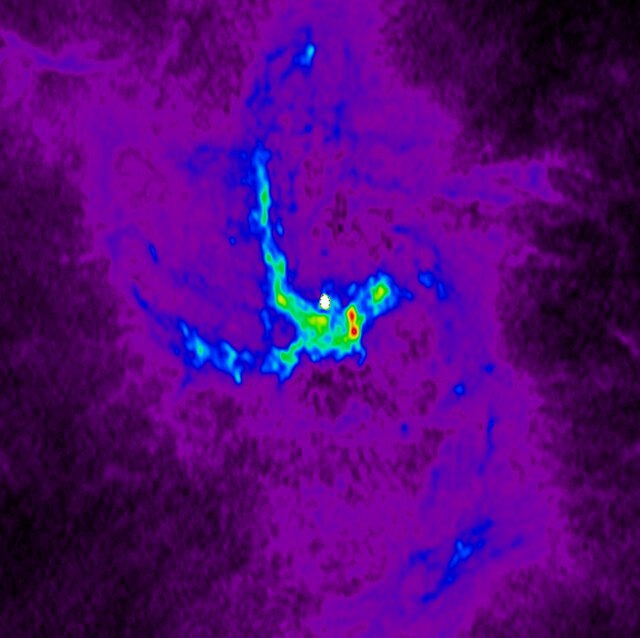
The black hole at the center of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A, has a mass about 4 million times that of the Sun. It’s also responsible for many activities, like regulating the formation of stars.

To successfully escape the pull of a black hole at the event horizon, a person will need infinite energy. The escape velocity near these freaks of nature is greater than the speed of light, so to successfully escape this predicament, one would need infinite energy to conquer the mass generated by moving at light speed.

Some supermassive black holes are super active, and their accretion disks are incredibly bright. These are known as quasars and can outshine entire galaxies.

There are many theories surrounding these marvels of the universe. Among them is the idea they can serve as a bridge between points in space-time; these bridges are called wormholes. However, there has been no observation of one.

Black holes are neither black nor holes. They are oblate spheroids for those that spin. For the ones that don’t spin, they are spherical. In fact, they are among the most spherical objects in the universe.
The time of death for a black hole the size of the Sun is 10^67. That’s far longer than the estimated time for a proton to decay, 10^34. For supermassive ones, it can take 10^100 years for it to eventually fizzle out.

Black holes contain the most entropy in reality; this means nothing else in the universe can ever have as much entropy as them.

Gravastars are an alternate idea that seems to solve the singularity problem of black holes. They have a similar look but are wild monsters with a pure pressure balance upheld by exotic dark energy. They have never been observed.
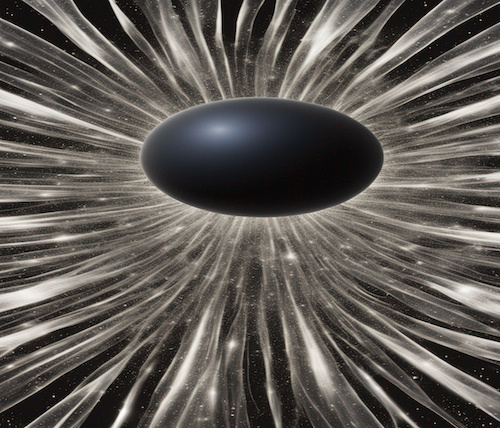

Gravastars could produce gravitational waves similar to those of the objects they aim to counteract; this can make them detectable through advanced observatories. Also, their proposed dark energy content could be the key to understanding the mysterious energy scientists believe overwhelmingly populates the universe.
According to current theoretical models, a person falling into a black hole cannot detect what’s occurring until they cross the event horizon, the point of no return.

If a person falls into a black hole, a distant observer will see them frozen in time at the moment they entered the event horizon; this is because the light from the person would be unable to escape.
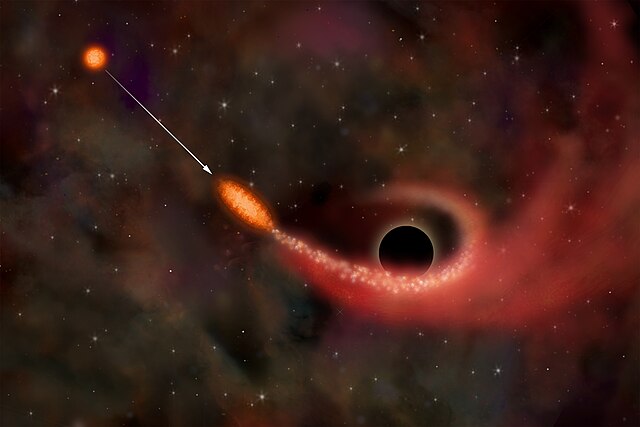

When a star gets too close to a black hole, it can be torn apart in a tidal disruption event, leading to a radiation flare.
Though they are the weirdest objects in the universe, black holes are made from normal matter, which condenses so tightly that it forms a gravitational pull stronger than the force of light.
What state of matter is a black hole? Even though they are formed from matter, they do not exist in any predefined state of matter; this is because the gravitational pull is so strong that atoms cannot exist in any state anymore. At the singularity, the density becomes infinite, and all laws of physics break down.
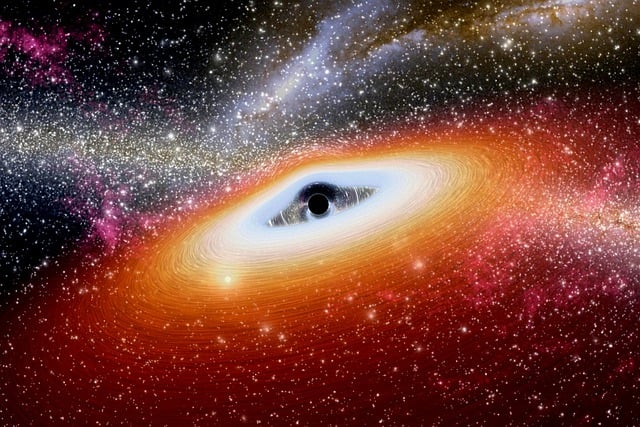

Just outside the event horizon, there is a region where light can orbit a black hole; this region is called the photon sphere.
DISCOVER OUR ARTICLES
Trending Animals and Nature Fiction Histories of the Past More on Nature Facts SnippetsLEARN MORE ABOUT US
Donate To Our Cause About Us Help Did You Enjoy Our Site? More Tags Coming Soon Our Goals Our Other SitesWIDEN YOUR KNOWLEDGE
Search Our Super Large Database Get Beautiful Pictures For Awesome Projects Back To Top© Fact Finder. All rights reserved.